Eurorack Voltages and Arduino
Introduction
Building Eurorack modules based on Arduino or Microcontrollers in generall opens up many new possibilities. Arduinos are e.g. cheaper than an AS3340 VCO, but can offer even more different waveforms when a wavetable is used. Furthermore, Arduinos can be used to interface digital synthesizer chips like the SN76489 or a YM3812 (often called OPL2).
Since the Arduino runs with 5V it is not possible to connect it directly to other Eurorack modules.
1V/Oct, CV, and Gates of the Arturia Beatstep Pro
The Beatstep Pro is a popular sequencer that can output midi as well as analog voltages according to the Eurorack standard. The output level ranges can be found in the user manual.
- 1V/Oct: 0V...10V (MIDI note range of 0...127)
- CV: 0V...10V
- Gate: 0V or 10V (V-trigger)
CV to ADC
The Arduino's ADC has an internal resistance of 100MOhm [1].
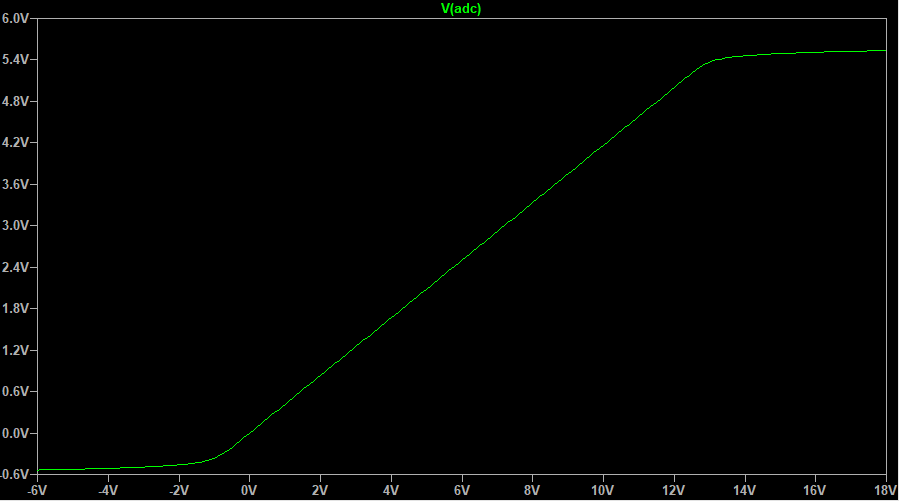
The Voltage at the CV input can be between -12V and 12V. Figure 1 shows a circuit that converts the levels to 0...5V.
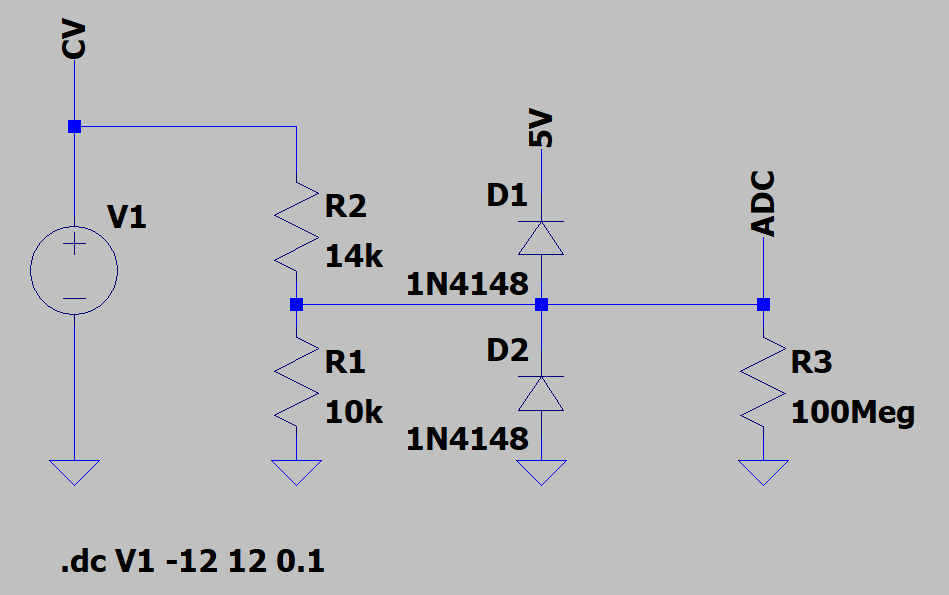
The schematic consists of a voltage divider (R2 and R1).
The diodes D1 and D2 are used to clamp the voltage V_ADC to a range between 0V and 5V.
1V/Oct to ADC
For 1V/Oct the same circuit can be used as for CV. The voltage resulution for a 10bit ADC is given by
![]()
The voltage difference of a semitone step is given for a 1V/Oct input by
![]()
Therefore the resolution of the ADC is sufficient.
Gate Inputs
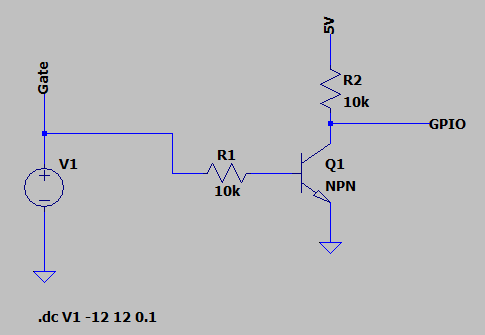
The circuit shown in Figure 3 can be used to convert the Gate levels to a value between 0V and 5V. For this transistor configuration a GPIO voltage level of 0V corresponds to High and 5V to Low. The resistor R2 can be left out if the internal pullup resistor of the microcontroller is used.
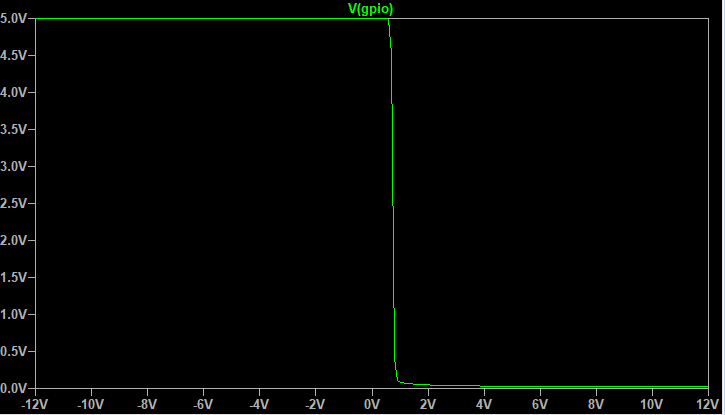
At a threshold of 750mV, the GPIO voltage switches from 5V to 0V.
References
[1] https://electronics.stackexchange.com/questions/250759/how-many-ohm-is-the-adc-port-internal-resistance-of-the-atmega8